What is a UX Audit?
UX Audit is a comprehensive process of evaluating the overall user experience of websites, software, or products to identify areas that need improvement.
It involves assessing the usability, accessibility, and aesthetics of the interface in order to provide actionable insights and recommendations that can be used to create an improved product.
The audit looks at aspects such as user flows, task completion rate, hardware compatibility, responsiveness on different devices and browsers, visual appeal, content clarity and organization.
Additionally, UX auditors analyze user feedback from surveys and focus groups in order to identify any further issues or opportunities for improvement.
Introduction to UX Audit
Potential customers come to your website or app through searches, social media, references, articles, or marketing campaigns.
They check out the website. Some people might install the app, explore the features, and try the service for a while but abandon the product after some time.
Or in some other cases, you have a product that has attracted some users initially. But you don’t see any growth in their numbers or usage. Also, you see users leaving your app or website or using it less frequently. Even if you invest a lot in marketing campaigns, you don’t see it reflected in usage or revenue.
One of the critical reasons for situations like this could be the poor user experience/user journey of your app or website.
The stakeholders might have some idea about the bottlenecks of the product performance.
Still, in most cases, they are confused, partially aware, or even clueless about what to change, how to change, and when to change within their product or service. This is where a professional UX audit comes to your rescue.
Let us look into the UX audit in detail.
The UX Audit recommends improvements to boost conversions, increase revenue, improve loyalty, reduce churn rate, bounce rate, cart abandonment, uninstalls, etc., by providing users with the best experience. Also, a UX audit can help in increasing product performance to a great extent.
What are the Benefits of UX Audit?
UX audit will help you answer the most pressing questions like:
- What works and what doesn’t work in an app or website? And why so?
- What insight does the data provide about user experience and usability?
- Which are the key metrics and KPIs to be monitored continuously?
- Strategies that have already been tried and their impact on metrics.
On top of answering these questions, a UX audit provides evidence-based, actionable recommendations and supports strategic design plans.
It helps develop usage metrics that will help better decision-making in the future. Also, you get to create hypotheses about user behavior that helps you in better prediction.
Once follow-up actions are taken, user experience audits can help drive conversion rates, and speed-up return on investment, by increasing product revenue, user satisfaction, user retention, and brand loyalty.
Usability Testing vs. UX Audit
Usability testing and UX auditing are two critical User Experience practices (UX). Usability testing is a technique for determining how simple it is for users to interact with a product or service, such as an app or website.
Participants are asked to complete specific tasks while experts observe their behavior and interactions with the product during usability testing.
This testing identifies any problems with the user interface, allowing developers to make any necessary changes before releasing a product. UX Audit, on the other hand, is a user-centered analysis of existing or proposed products and services.
Its goal is to identify areas for improvement in a product’s or service’s overall user experience.
Typically, the audit process involves researchers interviewing stakeholders involved in the development process, analyzing customer feedback, and reviewing industry design and usability standards.
Field visits and competitive benchmarking are examples of observational studies.
Usability testing and UX audits are critical components of the UX design process, as they help ensure that products meet the needs and expectations of users. Finally, both methods contribute to creating exceptional digital experiences that are enjoyable, efficient, and rewarding for all users.
Would you like to see what goes in for our UX audit report? Download the PDF
What’s a UI Audit?
The aesthetics of UI( User Interface) cease to matter when the interface does not facilitate any user-interface interaction. In a UX audit, the focus is on the experience, and in a UI audit, the focus is on the expression of the software in visual language. UI audit can also be used to trace out minor usability issues.
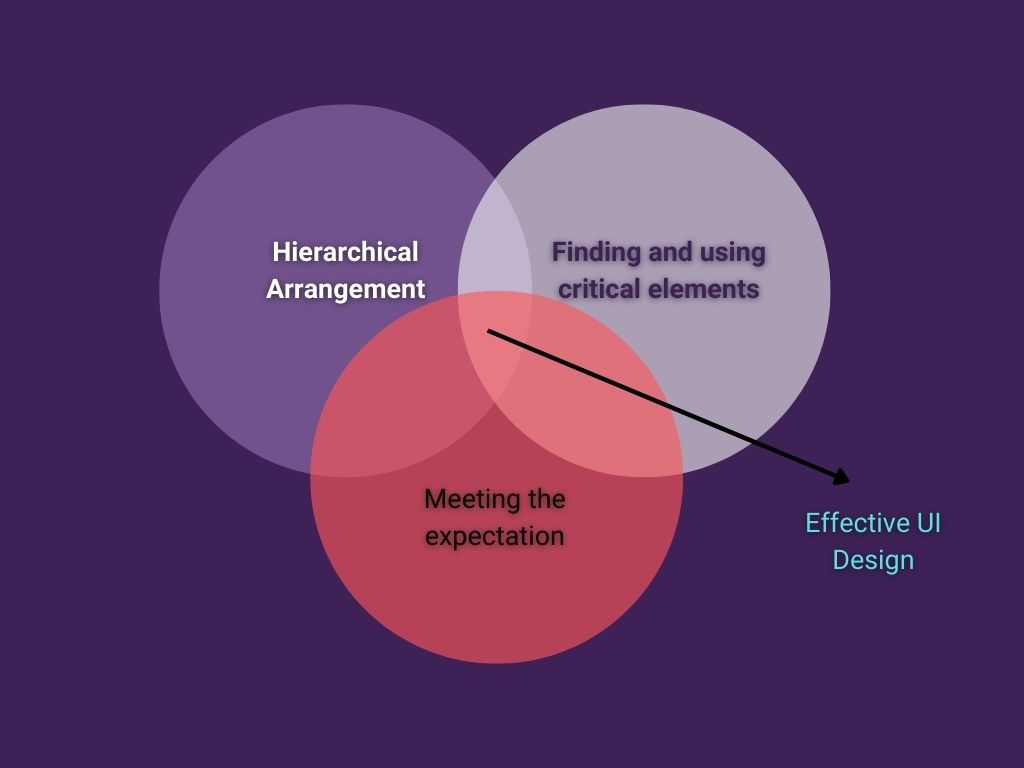
6 UX Design Principles You Need to Consider
- What is the user seeking from the product?
- Users are more comfortable with familiarity rather than with new experiments.
- Be in the shoes of users and find out the purpose of the software
- Using the right typography
- Where should the focus be on? Providing information or functionality?
- Giving more controls to users
Why Should a UX Audit be Conducted?
UX audit helps improve the user experience of a product and will, in turn, increase customer satisfaction as they no longer feel frustrated or confused.
The exercise will help stakeholders make decisions that are research and data-driven. This will reduce customer acquisition and support costs and increase CLV (customer lifetime value) and retention rates.
Who Should do a UX audit?
Organizations that do not have a dedicated UX team are likely to benefit the most from a UX audit.
This is because those organizations with an in-house team continuously evaluate the product and user experience.
For the best outcome, it is advised to have external UX agencies conduct the audit, as the internal team will find it difficult to detach from the product and tends to make biased judgments.
When to do UX Audit?
A UX audit can be conducted at many stages of the product’s life cycle to recognize the performance and usability issues at that time.
- During a redesign of the product – A UX audit will help to evaluate existing user flows and trace problems or distractions that prevent users from completing their goals.
- During the development and implementation of new features – Conducting a UX audit at this juncture will help to understand how feasible the new features are and how much the users need them.
- Validate new product design before development – UX audit can be conducted on novel product ideas (MVP) even before developing them into a project. This will help to make changes that will not cause significant time and budget losses.
Requirements for a UX Audit
A few requirements must be satisfied for a UX audit to be conducted satisfactorily.
- A team of professionals comprises UX researchers, UX designers, UI designers, Information Architects (content specialists), engineers, product strategists, marketing experts, and business managers.
- The goal for the audit should be set beforehand.
- A time duration until which the audit will be conducted should be fixed.
- Decide the resource allocation regarding workforce, time, and money dedicated to the audit.
How to Conduct UX Audit
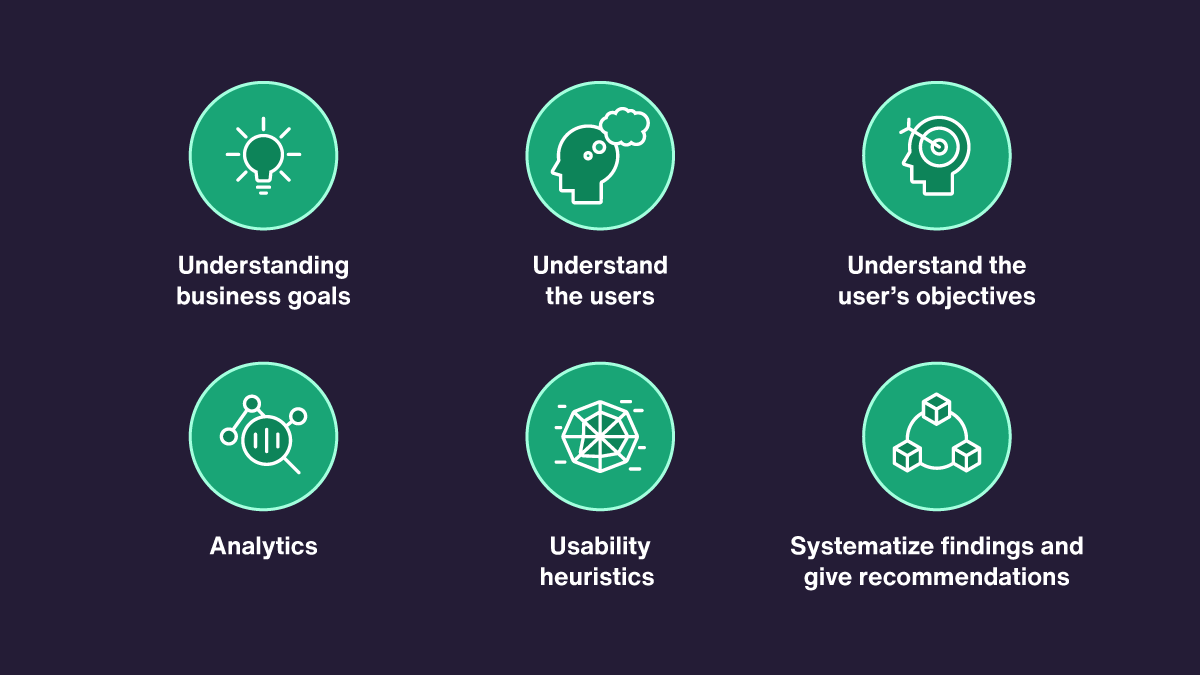
Even though there is no definite procedure since each organization or UX professional approaches it differently, depending on the product’s complexity, the scope of work, goals, the general steps undertaken in the audit, and the ultimate goals are often similar.
- Understanding Business Goals
Understanding the product and the organization’s business objective paves the foundation for conducting a UX audit. This knowledge helps determine the design audit’s objective and the product’s usability.
While surveys are conducted among stakeholders of the organization, covering every dimension of the product is a standard and quick process, interviews with key individuals of the organization, like product managers, developers, marketers, salespeople, customer service representatives, etc., are likely to give more insights into the product.
Each interview is conducted to gather information about the individual’s opinion of the positives and setbacks of the product.
The basic steps that should be taken to improve the product and grow the business are established from these individual viewpoints. It is not general business objectives that are derived from these interviews.
These interviews should define the new dimension of the organization’s set goals. These findings are more specific. For example, suppose the organization has set a goal to increase its sales. In that case, it can mean selling more of a particular product, increasing sales across the business, or driving in-store purchases.
The UX audit brings out the particulars of the goals defined. These findings are cross-checked with the organization to ensure they agree with the business objectives outlined.
- Understand the Users
To know the users better, user personas are created. Some organizations have an obvious idea about their customers which they might have collected from their research. This information can be used to make user personas representing the target customers.
The number of people interviewed is not fixed. In most cases, the selected persons for the interview are presented with the product and asked to share their experiences. Several interview protocols are available. These vary in the levels of detail and can be used according to preferences.
- Understand the User’s Objectives.
The information obtained from the users must be transformed into a user flow.
User goals are defined in different features and functionalities of the product. And the steps that should be taken to reach these goals are also described. This process must also identify areas where the user may encounter difficulties or get stuck.
This user should be based on information about user goals gathered from stakeholder interviews, user surveys, and user interviews.
- Analytics
Most organizations rely upon quantitative data from analytics tools like Google Analytics, Mixpanel, Woopra, etc. This data provides information about who interacts with the product and what they do there.
It is recommended to supplement the data from analytics with tools that perform different tasks such as heat mapping and other functions that provide advanced analytics. Whatever tools they use and how the product is used over time could be derived from the data collected.
- Usability Heuristics
Usability heuristics are a quick and practical way to solve problems or make decisions. In user experience (UX) design, professional testers use heuristic evaluation to determine the design/product’s usability systematically.
As experts, they use standard checklists to find deficiencies missed by the design team.
Heuristic evaluation is a process where experts use Nielsen’s ten usability heuristics to measure the usability of user interfaces in independent walkthroughs and report usability issues.
- Systematize Findings and Give Recommendations.
The data collected from the audit should be analyzed, condensed, and compiled into a report which communicates the findings to the stakeholders.
The report contains practical suggestions that provide specific solutions to the problems found during the audit.
It should be clear how each recommendation can be implemented and what it will do to meet business and user goals.
Findings and recommendations should be presented in the most effective way, which could be through site maps, wireframes, prototypes, or other visual means. Being overly critical while providing recommendations should be avoided.
Findings of a UX Audit
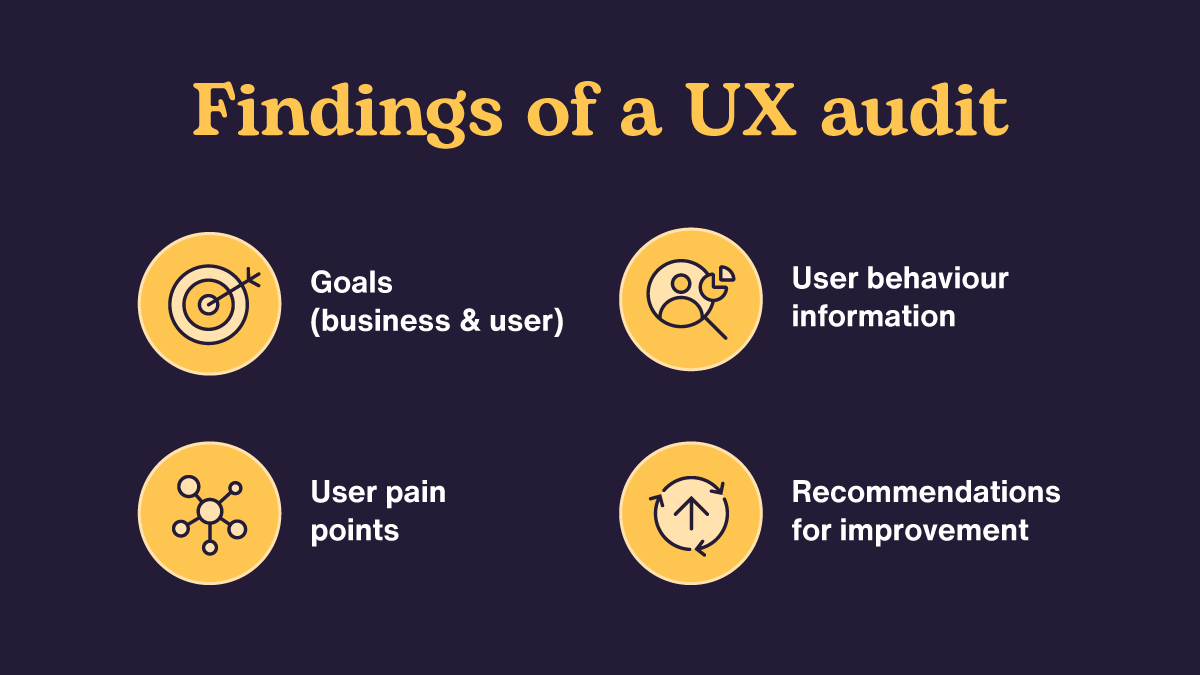
The report developed at the last stage of the UX audit constitutes different factors that together form the output.
- The report will specify the significant goals of the UX audit.
- The audit report gives detailed information about user behavior. Data from competitive analysis, user interviews, user testing, customer journey mapping, A/B testing, and heuristic evaluation will be included.
- The result of each of the tests will be described in detail. The user’s frustrations and pain points while using the product will be mentioned, with recommendations for improvements in potential areas.
- The recommendations and suggestions will be listed according to priority to get the best benefit from the UX audit conducted. This helps in quick decision-making.
- The format for the UX audit report is not fixed since its content and structure depend upon the complexity and requirements of each project.
Recommendations
The audit team will make recommendations to improve the product’s User Experience with all this information collected.
Ideally, the recommendations should:
- Data-driven
- Actionable
- Emphasize the positives.
- Express the annoyance tactfully.
- Avoid usability jargon.
- Be very specific.
The recommendations should be supplemented with examples rather than just identifying areas for general change.
For example, “in navigation drop-downs, remove images.”
UX Audit Tools
Many tools can help in measuring the UX of the software product.
Here are some
1 Mixpanel
Anyone can access robust analysis thanks to Mixpanel. With just a few clicks, you can query your data in interactive reports and quickly view visualizations.
This makes it simple to respond to endless inquiries about how your product is used, who stick around, and various other topics.
2. Analytics
Ok, this can look like an odd tool, but Google analytics can help you attain knowledge in user interaction.
There is a section in analytics called behavior where you see the behavior flow and determine which area of the web page is losing users more than others.
Also, you get to know details like bounce rate, user demographics, unique visitors, etc., which can help you with valuable UX information.
3. UserZoom
UserZoom is a robust user experience tool designed to help optimize website design, usability testing, and customer feedback. It provides advanced features such as creating surveys, moderating tests, facilitating A/B testing, and more.
UserZoom allows product teams to easily capture insights from users quickly and accurately, providing valuable data that can be used to improve the overall user experience.
With its intuitive design, quick implementation, and comprehensive analytics, it’s no wonder UserZoom continues to be a favorite among product teams around the globe.
4. HotJar
Hotjar’s UX Audit tool helps in evaluating the user experience of a website. This powerful, intuitive tool can be used to identify areas of improvement on a website or even pinpoint potential usability issues.
It allows users to measure user satisfaction and engagement, gather feedback from visitors about their experiences, and analyze key metrics such as clicks, taps, scrolls, and mouse movements.
Hotjar also provides a comprehensive report which includes heatmaps for visualizing user interactions with the website, session recordings for watching people interact with the site in real-time, and survey data to capture deeper insights from visitors.
With this information, UX professionals can make informed decisions on how to improve the overall design of their website and provide an unforgettable user experience.
5. Loop 11
The 11 Loop Tool is a powerful collaborative tool that enables users to track and manage their projects in a visual, organized way.
It allows users to create task lists, assign tasks to team members, set deadlines, add details and notes to tasks, track progress and dependencies, and more.
Combining project management features like Gantt Charts, Kanban boards, project calendar views, and task management portals into one comprehensive solution; the 11 Loop Tool simplifies the process of managing complex projects.
With detailed analytics and insight into performance metrics, it’s a handy tool for teams looking to stay on track with their goals.
Cost of UX audit
The cost of a UX audit depends mainly on the scope and complexity of the work, the people you work with (whether a UX agency or an individual freelancer), and the duration of the audit.
It will cost at least US$3,000 to US$5,000 for a basic UX audit that lists and explains usability issues. This could typically be done in a week or two.
For extensive usability reviews with detailed recommendations, which could take 2-4 weeks, established agencies may charge between US$8,000 to US$15,000.
Limitations of UX Audit
While a UX audit is a boon to resolving many UX woes, it doesn’t solve every problem. A UX audit is ineffective if recommendations are not actionable or not followed up. It also requires a significant investment of time and effort from the stakeholders. If this audit is conducted in-house, it can hurt the ordinary course of other tasks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a UX audit is vital to website development and maintenance. It helps to ensure that the website is designed for maximum usability and user satisfaction.
Through a comprehensive evaluation process, UX audits can identify potential issues in design, navigation, user interface elements, content layout, and other aspects of website development.
By addressing problems early on, companies can save time and money by avoiding future costly fixes or reworks.
Ultimately, this ensures better experiences for users and more successful online businesses.
Are you looking for someone to help you with your product’s UX audit? Let’s talk in Detail.